To achieve optimal performance of a benchtop power supply, it is important to understand its basic principles. A benchtop power supply converts the AC input power from the wall outlet into DC power that is used to power the various components inside a computer. It typically operates on a single-phase AC input and provides multiple DC output voltages, such as +12V, -12V, +5V, and +3.3V.
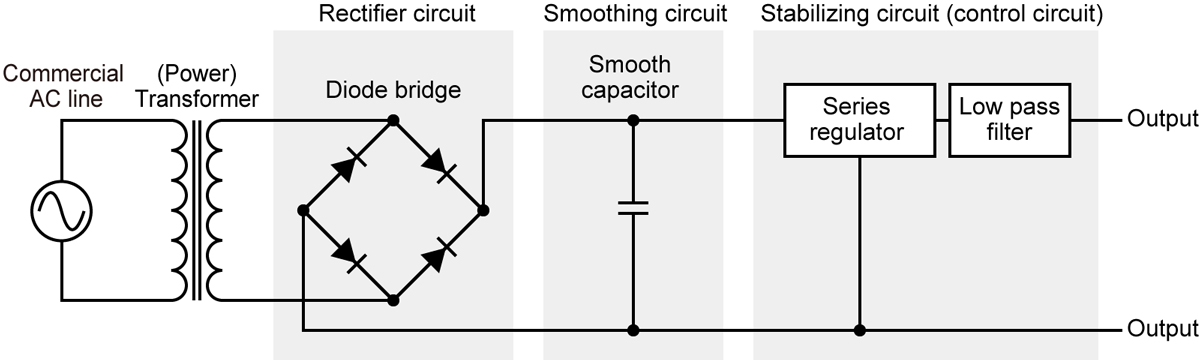
To convert the AC input power into DC power, a benchtop power supply uses a transformer to convert the high voltage and low current AC input power into a lower voltage and higher current AC signal. This AC signal is then rectified using diodes, which convert the AC signal into pulsating DC voltage.
To smoothen out the pulsating DC voltage, a desktop power supply employs capacitors that store the excess charge and release it during periods of low voltage, resulting in a more stable DC output voltage. The DC voltage is then regulated using a voltage regulator circuit to ensure that it remains within tight tolerances, preventing damage to the components. Various protections, such as overvoltage protection, overcurrent protection, and short circuit protection, are also built into desktop power supplies to prevent damage to the components in case of faults.
Understanding the basic principles of a desktop power supply can aid in selecting the appropriate power supply for the computer system and ensure optimal performance.
In this article, we’ll cover the basics of what a benchtop power supply is, how to use it properly, and what to look for when choosing a model.
What is a Benchtop Power Supply?
When you’re working on a project that requires a precise amount of DC power, a benchtop power supply can come in handy. Essentially a small power supply that’s designed to sit on your workbench.
These devices are also known as lab power supplies, DC power supplies, and programmable power supplies. They’re perfect for electronics for those who need access to a reliable and easy-to-use power source.
While there are several types of benchtop power supplies available–including ones with communication functions, multi-output types, and ones with various features–they’re all designed to make your operations easier and more accurate.
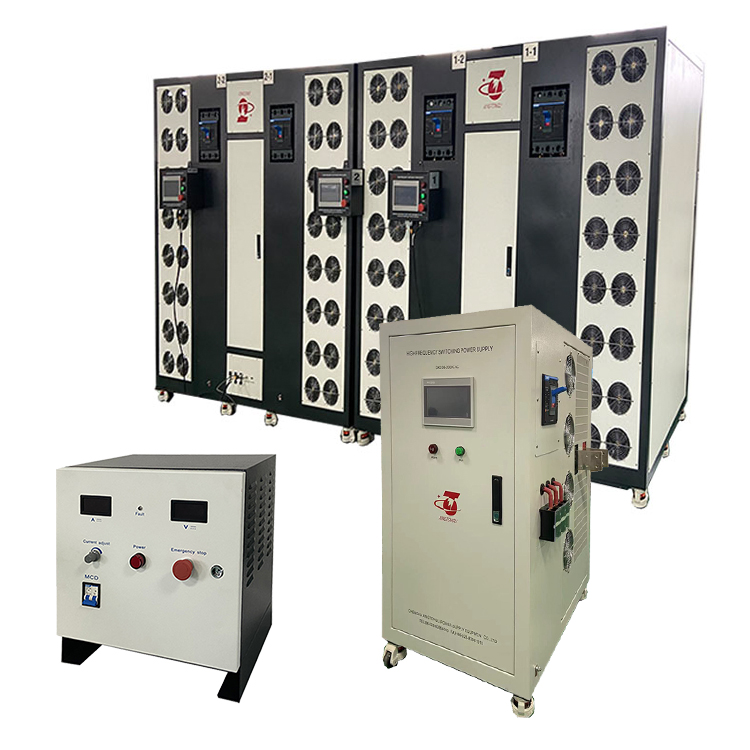

How does it work?
A benchtop power supply is a versatile piece of equipment that provides regulated power to electronic devices. It works by drawing an AC power line from the mains and filtering it to provide a constant DC output. The process involves several components, including a transformer, rectifier, capacitor, and voltage regulator.
For example, in a linear power supply, the transformer steps down the voltage to a manageable level, the rectifier converts the AC current to DC, the capacitor filters out any remaining noise, and the voltage regulator ensures a stable DC output. With the ability to adjust voltage and current levels and protect devices from over power, a benchtop power supply is an essential tool for automatic inspection systems, School training aid, etc.
Why is it important?
A benchtop power supply may not be the most glamorous piece of equipment in an electrical engineer’s lab, but its importance cannot be overstated. Without one, testing and prototyping will not be possible in the first place.
Benchtop power supplies provide a reliable and stable source of voltage for testing and powering electronic circuits. They allow engineers to vary the voltage and current to components to test their limits, observe how they perform in different applications, and ensure they will function correctly in the final product.
Investing in a quality benchtop power supply may not seem like the flashiest purchase. Still, it can make a significant impact on the success and efficiency of electronic design and development.
Post time: Jun-08-2023