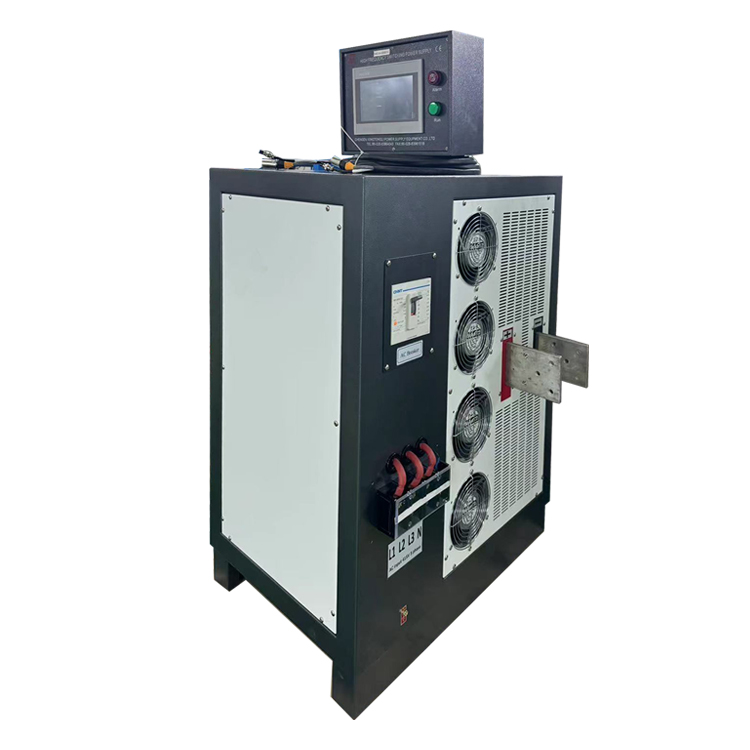
Copper rectifiers are essential components in various industrial processes, particularly in the electroplating and metal refining industries. These rectifiers play a crucial role in converting alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) for the electrolytic refining of copper. Understanding the working principle of electrolytic copper rectifiers is fundamental to comprehending their significance in industrial applications.
The working principle of an electrolytic copper rectifier involves the conversion of AC to DC through the process of electrolysis. Electrolysis is a chemical process that uses an electric current to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction. In the case of copper refining, the rectifier facilitates the deposition of pure copper onto the cathode by passing a controlled DC current through a copper sulfate solution.
The basic components of an electrolytic copper rectifier include a transformer, rectifying unit, and a control system. The transformer is responsible for stepping down the high voltage AC supply to a lower voltage suitable for the electrolytic process. The rectifying unit, which typically consists of diodes or thyristors, converts the AC into DC by allowing current flow in only one direction. The control system regulates the output voltage and current to ensure precise and stable conditions for the electrolytic refining process.
The process of electrolytic copper refining begins with the preparation of the electrolyte, which is a solution of copper sulfate and sulfuric acid. The anode, typically made of impure copper, and the cathode, made of pure copper, are immersed in the electrolyte. When the rectifier is activated, it converts the AC supply to DC, and the current flows from the anode to the cathode through the electrolyte.
At the anode, the impure copper undergoes oxidation, releasing copper ions into the electrolyte. These copper ions then migrate through the solution and are deposited onto the cathode as pure copper. This continuous flow of current and the selective deposition of copper ions onto the cathode result in the purification of the copper, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
The working principle of the electrolytic copper rectifier is based on the fundamental laws of electrolysis, particularly Faraday’s laws. These laws govern the quantitative aspects of electrolysis and provide a basis for understanding the relationship between the amount of substance deposited and the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte.
Faraday’s first law states that the amount of chemical change produced by an electric current is proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte. In the context of electrolytic copper refining, this law determines the amount of pure copper deposited on the cathode based on the current passing through the rectifier and the duration of the electrolysis process.
Faraday’s second law relates the amount of substance deposited during electrolysis to the equivalent weight of the substance and the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte. This law is essential in determining the efficiency of the electrolytic copper refining process and ensuring the consistent production of high-quality copper.
In addition to Faraday’s laws, the working principle of electrolytic copper rectifiers also involves considerations of voltage regulation, current control, and the overall efficiency of the refining process. The rectifier’s control system plays a critical role in maintaining the desired voltage and current levels, which are essential for achieving the desired quality and purity of the refined copper.
Furthermore, the efficiency of the electrolytic copper refining process is influenced by factors such as temperature, agitation of the electrolyte, and the design of the electrochemical cell. These factors can impact the rate of copper deposition, the energy consumption of the rectifier, and the overall cost-effectiveness of the refining operation.
In conclusion, the working principle of electrolytic copper rectifiers is rooted in the principles of electrolysis and electrical engineering. By converting AC to DC and regulating the voltage and current for the electrolytic refining process, these rectifiers enable the production of high-quality, pure copper for various industrial applications. Understanding the intricacies of electrolytic copper rectifiers is essential for optimizing the efficiency and effectiveness of copper refining operations in the modern industrial landscape.
Post time: Jul-19-2024